Low light leads to increased melatonin synthesis 54%
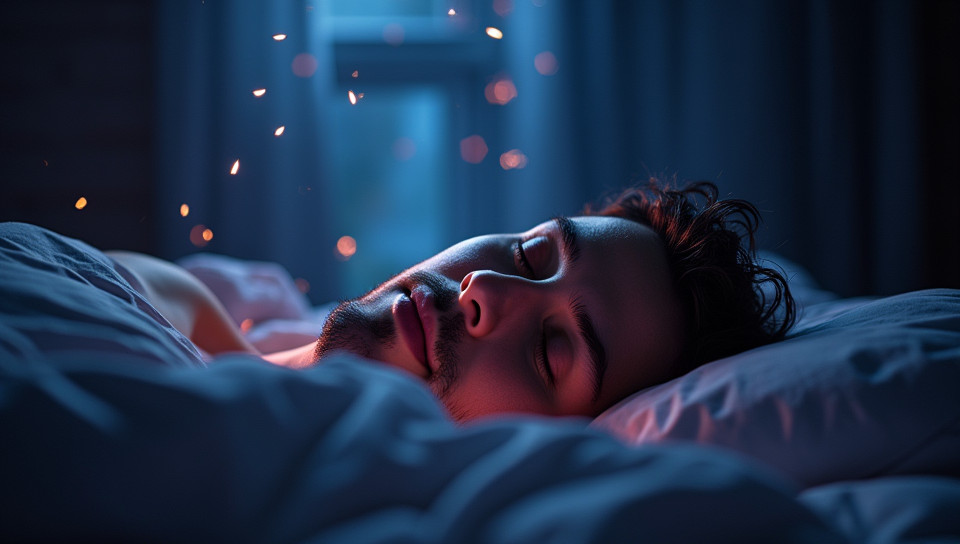

The Dark Truth About Melatonin Synthesis
As we navigate our daily lives, it's easy to overlook the subtle yet significant effects of low light on our bodies. But what if I told you that the dimly lit rooms and flickering streetlights are more than just a nuisance? They're actually triggering a crucial process in our brains – the synthesis of melatonin.
The Science Behind Melatonin
Melatonin is often referred to as the "sleep hormone." Produced by the pineal gland, it regulates our sleep-wake cycles and is essential for maintaining a healthy circadian rhythm. But what happens when we're exposed to low light levels? Research suggests that melatonin synthesis increases in response to reduced illumination.
The Role of Low Light in Melatonin Synthesis
- Reduced visual input stimulates the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), the part of our brain responsible for regulating our circadian rhythms.
- The SCN sends signals to the pineal gland, triggering an increase in melatonin production.
- As melatonin levels rise, we begin to feel drowsy and our sleep-wake cycle adjusts accordingly.
Implications for Our Daily Lives
So what does this mean for us? For one, it highlights the importance of maintaining a consistent light-dark cycle. Exposure to artificial light sources, especially in the evening, can suppress melatonin production and disrupt our natural sleep patterns. This has significant implications for our overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
Low light levels may seem like a minor annoyance, but they play a crucial role in regulating our melatonin synthesis. By understanding this process, we can take steps to optimize our sleep habits and maintain a healthy balance between rest and activity. So next time you find yourself struggling to fall asleep, remember – it's not just the bed that needs adjusting, but also the lights.
- Created by: Matías Meza
- Created at: Oct. 13, 2024, 7:05 a.m.
- ID: 12292